 |
|
Toll-Free 1-888-484-9560
Store Locator | NOW HIRING FOR NY STORES
Walker Oxygen Sensors
If your not sure what part you need for your vehicle
Please visit
our
Ebay store to find auto parts for your car or
light truck.
There you can easily search by year-make-model
![]()
The Walker Oxygen Sensors are precision made for outstanding performance and manufactured to meet and exceed all original equipment specifications and test requirements.
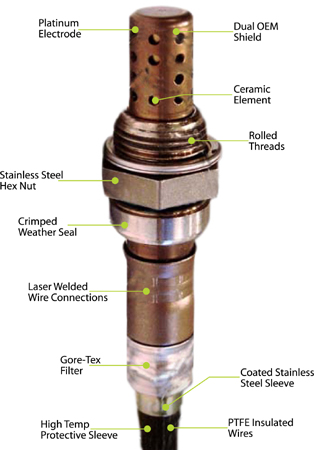
The oxygen sensor is a device which determines the oxygen content of the exhaust gas. Since the amount of oxygen in the exhaust gas is a very good indicator of combustion efficiency, it is also the best place to monitor the air fuel ratio. The ceramic sensor body is contained in a housing which protects it against mechanical effects and facilitates mounting. The ceramic body is made of stabilized zirconium dioxide (zirconia). The surface is coated with electrodes made of a gas-permeable platinum layer. In addition, a porous ceramic coating has been applied to the side exposed to the exhaust gas. This coating prevents contamination and erosion of the electrode surfaces by combustion residue and particles in the exhaust gases.
|
Features:
|
 |
What is the life expectancy of an oxygen sensor?:
30,000 to 50,000 miles is typical. However, constantly exposed to the harsh environment found in an automobile's exhaust system, the oxygen sensor must sustain a constant barrage of harmful exhaust gases, extreme heat and high velocity particulates, and that is under normal conditions. Sometimes contaminates such as coolant, oil, or silicone particulates will find their way to the sensor as well. This contaminates the sensor and renders it inoperable. An oxygen sensor's life is long in some applications up to 100,000 miles, but whether by contamination or normal use, its effectiveness will inevitably decrease over time.
When performing a vehicle tune-up, remove the oxygen sensor
and check for these symptoms:

Malfunctioning and failed sensors:
Oxygen sensors can fail when the sensor's ceramic element is exposed to certain types of silicone compounds or when an oil-burning engine leads to the sensor becoming oil-fouled. Also, a small amount of tetra-ethyl lead in the gasoline can kill an oxygen sensor. Over-the-counter fuel additives, which are not "oxygen sensor safe", can also kill an oxygen sensor. Failures can occur either: 1) instantaneously at the time the contaminant contacts the oxygen sensor, causing a dead sensor, or 2) gradually over a period of time. Gradual deterioration results in a "slow" sensor which does not react as quickly as it should, causing the catalytic converter to perform less efficiently. This can lead to premature failure of the catalytic converter. "Slow" oxygen sensors can cause a drop in fuel economy of 10-15% and cause excessive exhaust emissions and poor drivability. Unfortunately, the symptoms of a "slow" oxygen sensor are not always obvious to the vehicle owner, unless the vehicle fails an emission test, a decline in fuel economy is noticed, or drivability problems occur.




 And Get An Instant Coupon Code
And Get An Instant Coupon Code
